Generative AI:
Where Does It Fit into the Telecoms Jigsaw?Generative AI: Where Does It Fit into the Telecoms Jigsaw?
Although telecom companies have not historically been among the first to adopt new technologies, CSPs are now showing a great deal of interest in AI and machine learning in general to accelerate the transformation of enterprises. Though AI has applications in literally hundreds of areas of a CSP’s operations, it is frequently unclear where those applications will have the greatest impact. Given that it is a subset of AI technologies and capabilities, generative AI is on most CSPs’ radars.
This report explores the practical steps that CSPs can take in the near future, to give themselves the best opportunity of utilising generative AI in their businesses once the technology reaches a point of maturity and use cases become feasible.
Telecom’s Future: How AI and Generative Models Are Changing the Game
CSPs are at a critical juncture as industries throughout the world undergo unprecedented transformations. The telecoms sector is under tremendous pressure to completely transform due to several issues, including stagnating revenue, difficulty in delivering innovative user experiences, and an everincreasing strain on networks from the relentless demands of 5G.
While CSPs worldwide have been using artificial intelligence (AI) to tackle some of these issues in recent years, infrastructure and data management are still responsible for the majority of operating costs. Ground-breaking innovations have resulted from the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) into telecom operations; generative AI has shown to be a particularly transformative force. The telecom industry has seen several changes as a result of the introduction of generative AI, including improved customer experiences, network management, and service delivery.
Nowadays, a lot of attention is paid to how large language models (LLMs) affect AI. Because they can interpret linguistic patterns and links, they are able to mimic human conversational interactions and leverage the vast information to generate content. Text summarization, content creation, speech recognition, image annotation, coding, sentiment analysis, and a host of other applications are among the many uses for them. Leading international companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft use LLMs for chatbots, NLP, content creation, and other tasks. Many use cases and industries, including healthcare (drug development), IT (data analysis), retail (product recommendations), and more, can benefit from the application of LLMs.
The most widely used LLMs nowadays are Gpt-3.5, Gpt-4, PaLM 2, Claude V1, Cohere, Falcon, and LLaMA; each has pros and cons of its own. For instance, Gpt-4 can perform sophisticated coding, comprehend complex thinking, and possess abilities that are comparable to those of a human. The fastest AI system is Gpt-3.5; PaLM 2 is an expert in reasoning; Claude V1 can assist in creating effective AI assistants; Cohere is beneficial for generating AI use cases; Falcon is intended for commercial use; and LLaMA is the most effective for fine-tuning.
Potential Business Models of Generative AI
Innovative business models for Generative AI include licensing subscription models that may be used by companies to produce their own content/code. For instance, OpenAI has licensed its GPT-4 language model to multiple businesses, and these businesses are utilising it to develop a range of products and services, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and content creation tools. Charging access to generative AI services, via Model as a Service (MAAS), which may be used by companies and people to produce content or to train generative AI models, is another business strategy where enterprises charge for every query on a specific model, that helps in planning for costs associated with each query. For instance, Midjourney is a platform that charges a fee to allow users to employ generative AI to create realistic images and paintings. Businesses can also utilise generative AI capabilities for growing transactional revenues by simulating outcomes via synthetic data that can be used to train machine learning models and recommend actions for goal optimisations. This synthetic data can be used to improve the accuracy and performance of machine learning models, which can lead to increased revenue for businesses, for example, to increase GMV on a marketplace of digital services. Moreover, generative AI can be embedded into existing systems to enhance capabilities and drive operational efficiencies that may result in overall cost savings that can be monetised by vendors. This is typically seen in network and energy optimisation and planning.
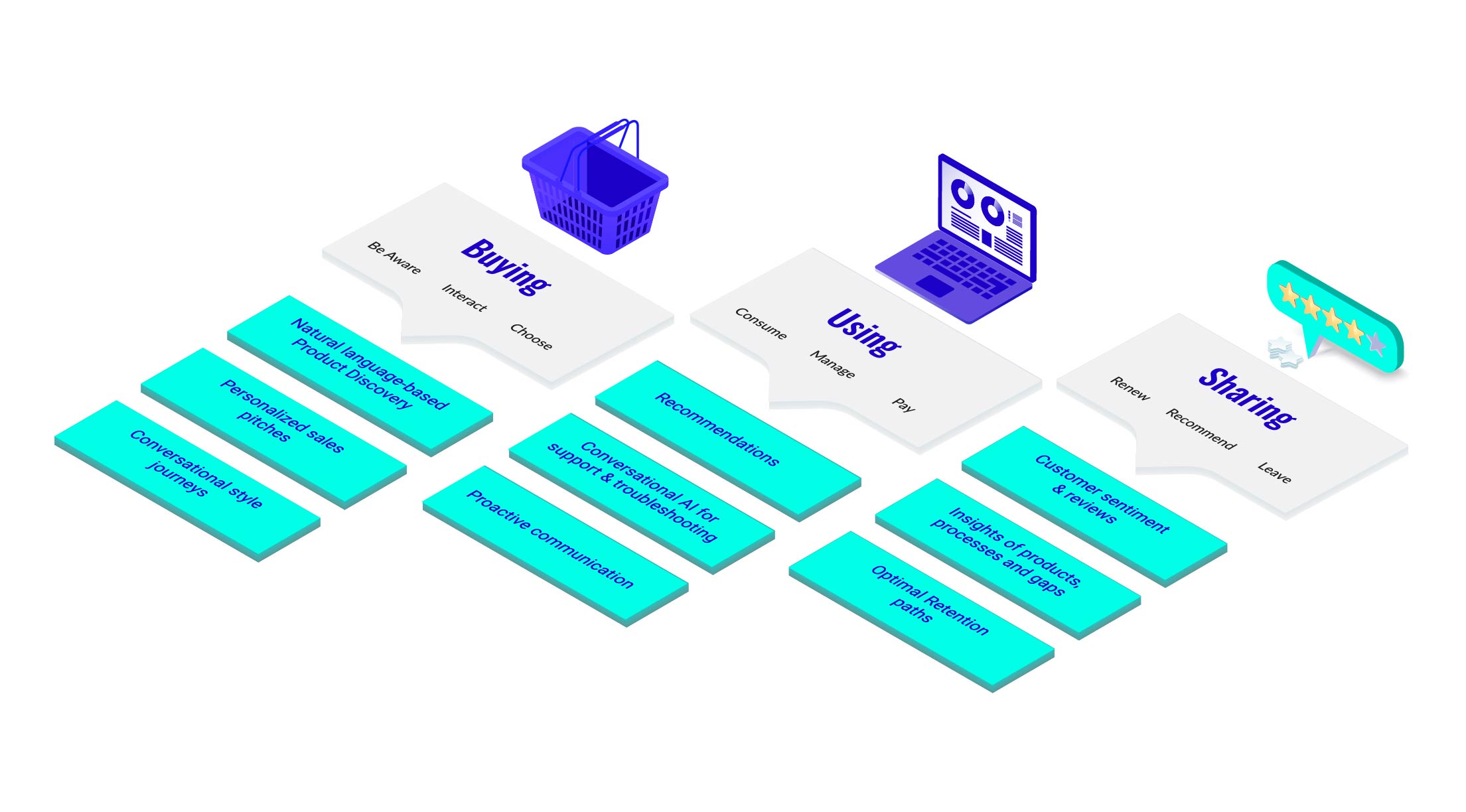
Use Cases of Generative AI in Telecom
It is obvious that generative AI has great potential to open up new growth and innovation channels for the telecom sector. To set the stage for a time when intelligent systems improve consumer experiences and boost efficiency, CSPs should use GenAI. At the moment, telecom companies can position themselves to take full advantage of application cases for generative AI.
- AI-Generated Content for Customer Support: Generative AI could be used to create detailed and easy-to-understand support documents, troubleshooting guides, or instructional content that helps customers set up and manage their services and devices.
- Virtual Network Design Assistants: Large Language Models with generative capabilities could assist network engineers in designing and optimizing network infrastructures by suggesting configurations, anticipating potential issues, and generating network design options based on best practices.
- Automated Contract Generation and Review: Leveraging Generative AI, the operator could automate the creation of custom contracts for enterprise clients, including service level agreements (SLAs), by inputting a few key parameters. The same AI could assist in reviewing contracts to ensure compliance with regulations and company policies.
- Personalized and Dynamic Marketing Campaigns: GenAI can generate highly personalized marketing copy and messages that resonate with individual customers. It could tailor promotions and advertising campaigns to each customer’s usage patterns, preferences, and feedback.
- Synthetic Data for Testing and Development: Generative AI could be used to create large datasets of synthetic data resembling actual customer usage patterns, which can be used for testing new services, applications, and software updates in a privacycompliant manner.
- Voice and Chatbot Personalization: Implement GenAI-driven chatbots and voice assistants that can generate human-like interactions, providing personalized support and upsell suggestions based on the customer’s history and the context of the conversation.
- Network Security Threat Simulation: Use Generative AI to simulate potential security threats and generate attack scenarios for training cybersecurity systems and teams, thus better preparing for real-world challenges and enhancing network security.
- Customizable 5G Services: Use Generative AI to create customized solutions for enterprise customers, generating network solutions that best fit their specific needs for 5G applications, such as IoT, AR/VR, and smart factory deployments.
While short-term opportunities for generative AI solutions focus primarily on customer service (chatbots, content creation, etc.), in the next couple of years, there will be numerous use cases for generative AI in product development (e.g., translation assistance) and operations (e.g., expanding customer service use cases into areas like billing, and improving website content or employee relations use cases).
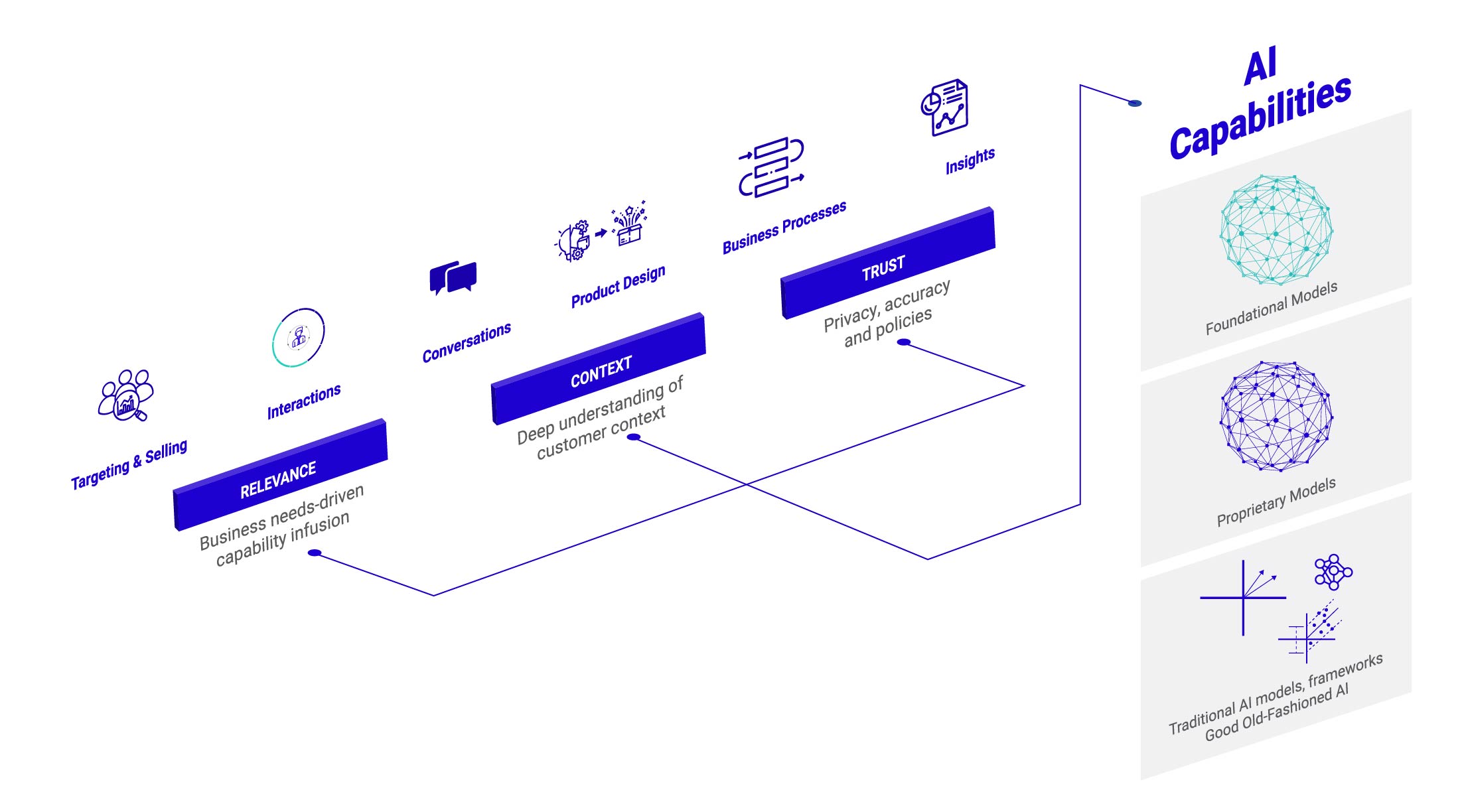
Generative AI Risks and Governance
Despite the exciting opportunities Generative AI offers, several risks need to be mitigated. From how to incorporate trusted, highquality models to finding technology providers and skills that will enable application development with these models, telecommunications companies need to be aware of the risks that Generative AI projects can go over budget, or even fail to deliver on their promise.
First and foremost, privacy and data security risks need to be managed. Generative AI models require vast amounts of data for training, and the sensitivity of this data can pose a serious risk if not properly secured. The highest value Generative AI use cases like customer personalization and network optimization will require the use of proprietary data, which will, in turn, require data security and privacy capabilities - potentially novel capabilities given the extent of the use of Generative AI models.
Another set of risks revolves around the trust and governance of the insights produced by Generative AI-powered models and applications. Are they accurate, fair, explainable, non-biased, robust, etc. The risk of bias in the AI algorithms, for example, can result in unfair or discriminatory outcomes. As it relates to the governance of Generative AI solutions, can endusers report on these measures of trust - and more - to regulators, risk managers, compliance officers, and auditors? Telecommunications companies need to ensure their AI models are transparent, assessed for technical performance and trust, and governable for a range of constituents.
One of the critical aspects of any generative AI solution, especially one that is being used in front-end engagement with customers, is ensuring trust in the output. Generative AI solutions are prone to hallucinations wherein outputs inferred from large sets of data can result in incorrect inferences. As such, it is critical to ensure a control framework is put in place to ensure the models do not generate incorrect information when a feasible output is not available. Similarly, the outputs operate within the guidelines and compliance of the enterprise’s policy to ensure that the generated information does not negatively impact the enterprise brand.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a disruptive force that is poised to help telecom companies improve network performance, enhance consumer experiences, and unlock new revenue streams. Leading telecom organizations are starting to develop generative AI roadmaps in collaboration with technology companies and AI platform vendors in efforts to develop trusted solutions that can drive business value like cost savings, revenue, and customer satisfaction.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Himmat Singh Gill
Vice President of Sales at Tecnotree
Himmat Singh Gill, Vice President of Sales at Tecnotree, is a seasoned leader with a proven track record in strategic sales. A distinguished alumnus of IIM Calcutta , he brings a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the telecommunications industry. His visionary leadership drives Tecnotree's commitment to empower MVNO's through the convergence of AI and 5G technologies with a focus on strategic differentiation, enabling MVNOs to succeed by tailoring services to diverse sectors, including Healthcare, Edutech, Fintech, Gaming, Betting and ensuring MVNO's stand out in a competitive landscape through tailored and differentiated services.



















